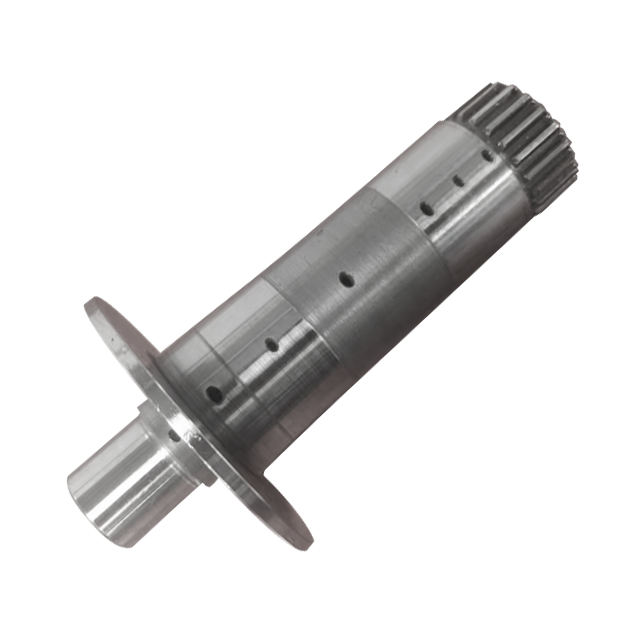
The PSA intermediate shaft machining line is designed to ensure high-quality and precise component manufacturing. An intermediate shaft machining line refers to a production facility or assembly line specifically designed to manufacture and process intermediate shafts used in internal combustion engines. The intermediate shaft is a critical component that connects the crankshaft and camshaft within an engine, facilitating the synchronised operation of various engine parts.
The machining line executes a sequence of precision machining operations, including turning, milling, drilling, and other processes, to shape, refine, and finish the intermediate shaft according to precise engineering specifications. This dedicated production line is equipped with specialised machinery, tools, and automated systems to ensure the accurate and consistent production of intermediate shafts with high-quality and precision.
The client
The client is an India-based leading high-precision components manufacturing company with a legacy of over six decades. Specialising in the manufacture of components for diverse industries such as the automotive, infrastructure, aviation, and windmill sectors, its product portfolio includes fasteners, power train components, sintered metal products, iron powder, cold extruded parts, water pumps, and radiator caps. The company’s global presence serves customers in India as well as markets in China, Germany, the USA, and the UK, among others.
Highlights of the case
Our client was seeking automation for the PSA intermediate shaft machining line. Automation in the machining line can provide many benefits, such as accuracy in production, enhanced efficiency and production, reduced human error, increased safety of shop floor workers, and more. Our client aimed to achieve all these benefits with our help.

Challenges and requirements of our client
Our client faced numerous challenges in their existing production process, such as:
- Acquiring skilled manpower capable of operating the machinery effectively
- Ensuring product accuracy
- Maintaining a consistent production rate
- Achieving optimum utilisation of resources
- Ensuring operational convenience
- Ensuring shop floor safety
- Automatic door open/close with confirmations
- Maintain a clear space for easy access during loading and unloading processes
- Spindle orientation in all turning cells
- Automatic job clamp/unclamp mechanisms
- Component seat and clamp confirmation machine
- Jig wash and flush coolant systems for chip removal at the machining area
- Ethernet connectivity for the interface with the machines
m2nxt solution
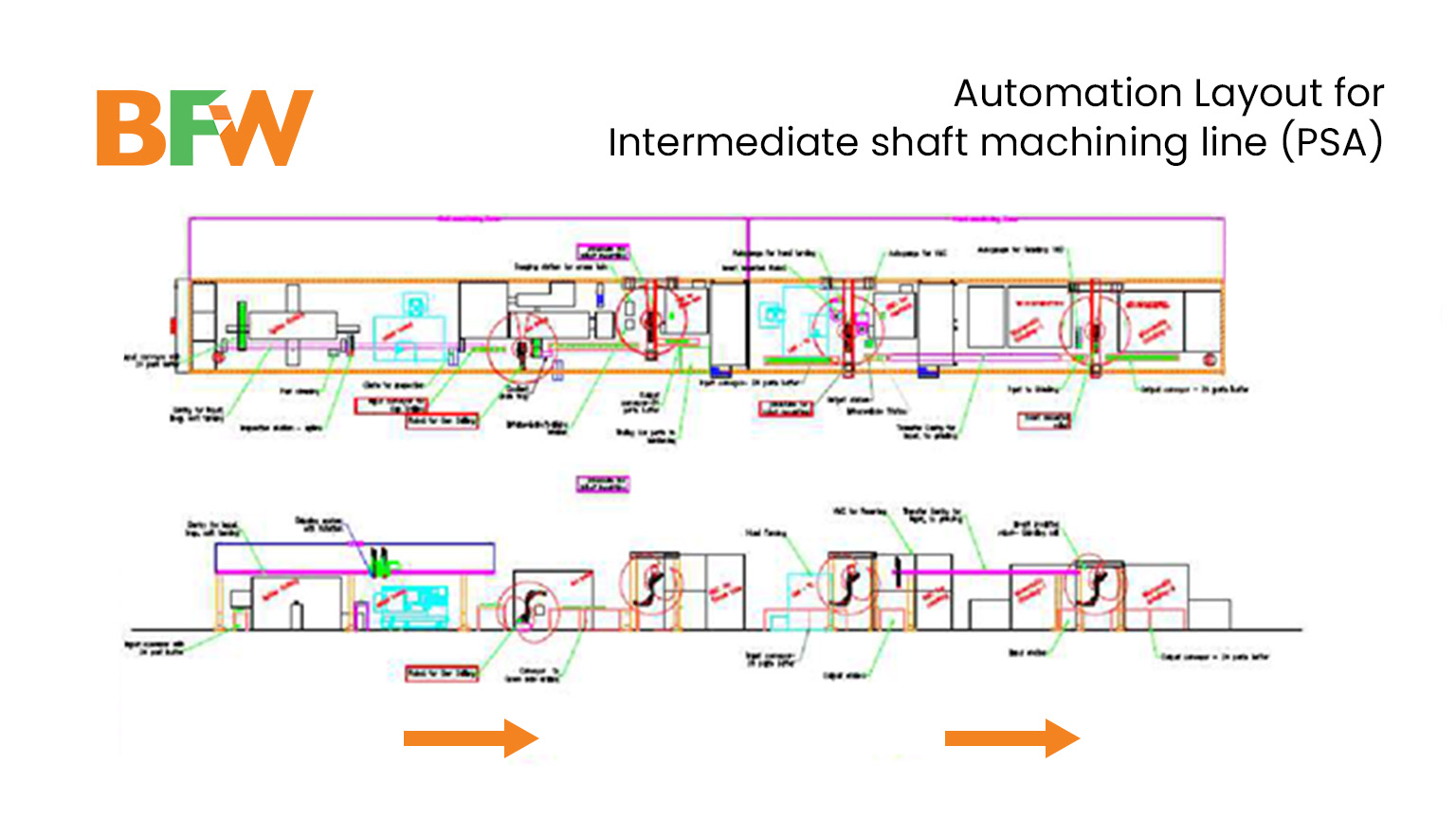
BFW subsidiary company m2nxt, provided a robust automation solution. The solution comprised several key components designed to optimise efficiency and productivity across the production line.
The line was structured with various cells, each serving a specific function. For instance, in Cell No. 1, we integrated a spline rolling and a soft grooving machine.
Next, to facilitate the seamless handling of parts, we implemented a three-axis servo gantry system featuring one horizontal axis and two vertical axes. Here, each vertical axis was equipped with a gripper for part manipulation and a rotation unit to facilitate orientation changes between machines. An input conveyor designed as a slat type with a capacity of 24 parts ensured smooth material flow.
Additionally, there was a part cleaning station and an inspection station equipped with linear slides for four varieties of spline checking gauges. Then, we strategically placed a reject bin for defective parts and ensured quality control.
Following inspection, parts could be transferred to the soft turning machine for further processes. The system also facilitated the loading and unloading the parts from the soft-turning machine.
The turned parts could be moved via the gantry system to the subsequent cell with the gun drilling machine. Here, an interface panel featuring PLC/HMI capabilities was integrated to facilitate communication and control between machines, robots, and peripheral equipment.
Furthermore, to prioritise shop floor safety, safety fences were installed in compliance with safety regulations and to minimise accidents.
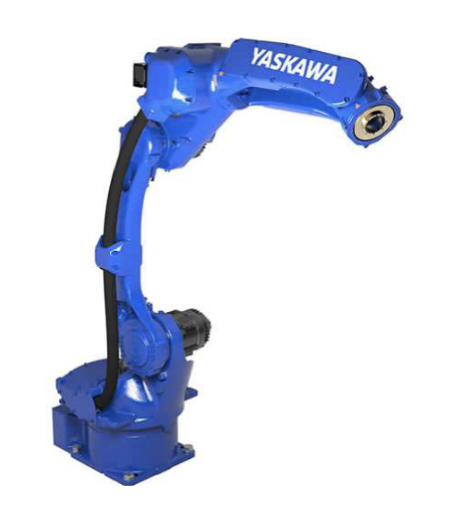
Considering the payload and reach requirement, we selected Yasakawa Make GP-12 and GP 25.

Impact
- Cycle time estimation: We estimated that each machine’s load/unload process would take approximately 18 seconds. However, this duration may vary based on factors such as machine configuration and approach. According to the cycle time provided, the robot is anticipated to wait for the machine during operation. Our client must communicate any alterations to the manufacturing process cycle time. Fixture cleaning is assumed to occur after removing each fresh part from the machine, while the opening and closing of machine doors are excluded from this cycle time calculation.
- No skilled labour required: Our automation solution eliminated the need for highly skilled labour, as machines now handle tasks previously performed manually. This reduced dependence on specialised workforce and minimised recruitment challenges and training costs.

- Consistency in production rate and quality: With automation, production processes were standardised and controlled, leading to consistent output in both rate and quality. Machines perform tasks with precision and repeatability, reducing variability and ensuring uniformity in the manufactured components.
- Zero rejection: Automation minimises human error and enhances accuracy, drastically reducing rejected parts. The stringent control mechanisms integrated into automated systems ensure that components meet quality standards consistently, leading to virtually zero rejection rates.
- Better ROI: Automation leads to improved efficiency, productivity, and reduced operational costs over time. The return on investment in automation technologies is significantly enhanced with consistent production rates, higher throughput, and lower rejection rates. Moreover, reduced reliance on labour translates to long-term savings in labour costs.
- Less space consumption on the shop floor: Our automation solution was designed to be compact and efficient, utilising space more effectively than traditional manufacturing setups. By consolidating processes and optimising equipment layout, our automation solution minimised space requirements on the client’s shop floor, allowing for better utilisation of the client’s available space for other purposes or expansion opportunities.
Conclusion
In summary, the automation of the PSA intermediate shaft machining line has brought about transformative outcomes for our client, including reduced reliance on skilled labour, consistent production rates and quality, virtually zero rejection rates, improved ROI, and optimised space utilisation on the shop floor. These benefits underscore the effectiveness and value of automation in modern manufacturing environments.










