Non APC HMC For Machining Lines
- Home
- Products
- Horizontal Machines
- Non APC HMC For Machining Lines
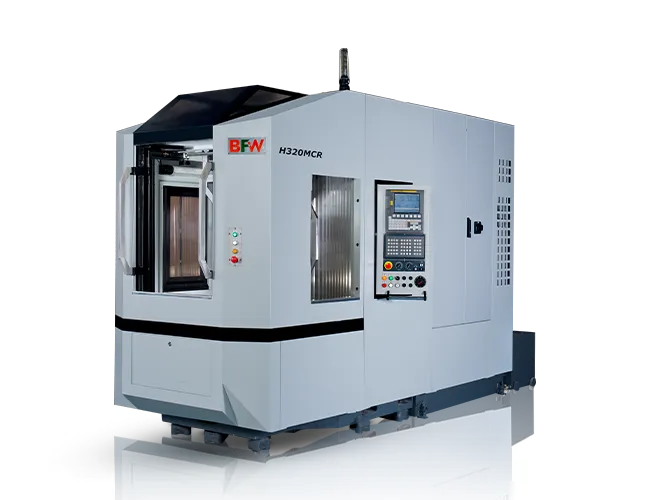

“The fast, flexible, and compact MCR series are loaded with many advantages including easy accommodation in machining lines, quick installation, and single lift facility. It also offers option of pallet changer-less configuration. Sustained accuracy, roller guide-ways, option of linear scale feedback, Ram-type spindle are the advantageous features that helps to meet the requirement of machining power train components of passenger cars and light commercial”.
Brand Story
High speed HMCs – It is specially designed for the production line requirements of the Automotive industry.
- Standard Features
- Unique Features
- Optional Features
- A narrow-width machine, easily accommodated in the machining lines.
- Automation friendly design
- Option of pallet changer-less configuration with various tables such as NC table, rotary table, tilting table, etc
- Option of various table configurations such as only B-axis, only A-axis, A+B or 5-axis, etc.
- Supports MQL technology
- Collision detection sensor
- iToolCaptain, BFW’s high precision tool monitoring system.
Watch MCR Live In Action!
Specifications
INDEX TABLE
| Specification | Unit | H 320 MCR | H 400 MCR | H 500 MCR |
| Index Table | ||||
| Pallet size | mm x mm | Dia 320 (Dia 400) | Dia 400 (Dia 500) | Dia 500 |
| Pallet type | Tapped holes with butting pads | |||
| Maximum load on table | kg | 300 (400) | 300 (500) | 650 |
| Pallet height from ground level | mm | 950, with 100 mm ground clearance | 1200, with 100 mm ground clearance | 1080, with 100 mm ground clearance |
| Maximum job swing - diameter x height | mm | 700 x 500 | 560 x 500 (800 x 500) | 700 x 700 (900 x 700) |
| Index positions | º | 360 x 1º (360,000 x 0.001º) | ||
Spindle & Axes
| Specification | Unit | H 320 MCR | H 400 MCR | H 500 MCR |
| Axes | ||||
| X/ Y/ Z | mm | 500/ 350/ 350 | 500/ 400/ 400 | 500/ 550/ 500 |
| Table top - spindle centre distance | mm | 100-450 | 100-500 | 170-720 |
| Table centre - spindle face distance | mm | 100-450 | 100-500 | 200-700 |
| Feed rate | mm/min | 1 - 40,000 | 1 - 20,000 | 1 - 20,000 |
| Rapid traverse X/ Y/ Z axis | m/min | 60 | 50 | 60 |
| Spindle | ||||
| Power cont./ int | kW | 3.7/ 5.5/ 7.5/ 11 | 5.5/7.5 (7.5/ 11) | |
| Speed (max.) | rpm | 8,000 (10,000) (12,000) | 8,000 (10,000 | |
| Taper | type | BT 30 (HSK A50) | BT 40 (HSK A63) | |
| Maximum torque | Nm | 35 with Siemens (58 with Mitsubishi) (70 with Fanuc) | 57 with Siemens (70 - with Mitsubishi/ Fanuc) | |
| Spindle- High torque(with Fanuc only) | ||||
| Power cont./ int | kW | NA | NA | 22/37(15 %ED) |
| Speed (max.) | rpm | NA | NA | 14000 |
| Taper | type | NA | NA | HSK A63 |
| Maximum torque | Nm | NA | NA | 250 |
AUTOMATIC TOOL CHANGER
| Specification | Unit | H 320 MCR | H 400 MCR | H 500 MCR |
| Automatic Tool Changer | ||||
| Pull stud | As per MAS-403 P30T-I | As per DIN 69872 | As per DIN 69872 | |
| Number of tools | Nos | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Maximum tool diameter with adjacent pockets full/ empty | mm | 80 | 80/ 125 | 80/ 125 |
| Maximum tool length - BT (HSK) | mm | 200 (300) | 250 (350) | 320 |
| Maximum tool weight | kg | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Tool changing time (tool to tool) | s | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Minimum C-C time as per ISO 10791-9 | s | 3.9 | 4 | 5 |
INSTALLATION DATA
| Specification | Unit | H 320 MCR | H 400 MCR | H 500 MCR |
| Installation Data | ||||
| Machine weight | kg | 5,500 | 6,500 | 8,500 |
| Total connected load | kVA | 25 | 45 | 55 |
| Floor area (for std machine) L x W | mm x mm | ~1,400 x 4,200 | ~1,700 x 4,650 | ~1,900 x 4,100 |
| Compressed air | bar | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Power supply | 415 V AC, 50 Hz, 3 Phase | |||
CNC Sistem
| Specification | Unit | H 320 MCR | H 400 MCR | H 500 MCR |
| CNC System | Siemens 828D / Mitsubishi M80/ Fanuc 0i MF | |||
Applications




Non APC HMC For Machining Lines
Have Any Question?
Non-APC HMC Machining Lines are Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) that do not include an Automatic Pallet Changer (APC) system. In a typical HMC equipped with an APC, the machine can swap out workpieces automatically, minimising downtime between operations by allowing an operator to load a new part while another is being machined. However, in Non-APC HMCs, this pallet-changing feature is absent, meaning the machine requires manual intervention to load and unload parts between machining cycles.
Key Features of Non APC HMC Machining Lines
- Manual Load/Unload Operations: Since there is no automatic pallet changer, the operator must manually load and unload parts, which can increase downtime between machining cycles. This typically results in a slower production process, especially in high-volume manufacturing environments.
- Lower Cost: Non-APC HMCs generally have a lower initial cost compared to CNC machines with automatic pallet changers. This can be a cost-effective solution for companies or shops that do not require continuous, high-volume production or where cycle times are less critical.
- Simpler Setup: Without the complexity of an automatic pallet changer, Non-APC HMCs are simpler in design and operation, reducing the learning curve for operators and maintenance requirements. This can be advantageous for smaller production runs or less complex operations.
- Flexibility for Small-Batch or Job-Shop Environments: Non-APC HMC machining lines are well-suited for smaller job shops, custom manufacturing, or environments where part variety is high and volume is low. Operators can easily switch between different parts, and the lack of an APC provides more flexibility in handling unique or small-batch jobs.
- Applications for Complex, Low-Volume Parts: Non-APC HMCs are often used in industries that deal with complex parts but do not require high-volume, continuous production. For example, tool and die shops or prototype manufacturers may prefer Non-APC HMCs as they are more focused on precision rather than performance and speed.
- Focus on Precision and Versatility: While the absence of an APC affects the speed of operation, the core capabilities of the HMC—such as multi-axis machining, precision, and the ability to handle complex parts—remain intact. Non-APC HMCs can still deliver excellent results in terms of accuracy and surface finishes, making them suitable for industries like aerospace, medical devices, and custom machinery where precision is key.
Applications of Non-APC HMC Machining Lines
Non-APC HMC Machining Lines are useful in various manufacturing settings where high-volume production and automation are not the primary concerns. For example:
Job Shops and Custom Manufacturing: Non-APC HMCs provide flexibility in job shops that handle a variety of parts with different designs. These shops often deal with smaller production runs or one-off jobs, so the absence of an automatic pallet changer is less of an issue. Operators can manually load different parts as needed, making these machines ideal for custom manufacturing or batch jobs where precision and versatility are more important than speed.
Prototype and R&D Manufacturing: For companies focusing on research and development, prototyping, or initial runs of new products, Non-APC HMCs allow for efficient handling of small quantities of parts. The ability to manually adjust setups for different designs makes these machines highly suited for environments where part changeovers are frequent and the focus is on testing designs rather than high-output production.
Tool and Die Making: Non-APC HMCs are often used in tool and die shops where the emphasis is on producing highly precise, low-volume parts like moulds, dies, and specialised tools. These machines offer the necessary precision and multi-axis capabilities without the need for continuous pallet changing, which is typically not essential in tool and die applications where production volumes are low and setup times are less critical.
Aerospace Components (Low-Volume): In the aerospace industry, Non-APC HMCs are often employed for machining complex, low-volume components. Parts such as landing gear components, brackets, or custom parts for aircraft that require multi-axis machining and precision are often produced on Non-APC HMCs. For these parts, setup times are less important than the quality of the machining process, and the manual loading of parts is a reasonable trade-off.
Medical Device Manufacturing (Custom or Low-Batch): Non-APC HMCs are also used in medical device manufacturing, particularly for custom or low-batch orders of devices like surgical instruments, implants, and specialised medical tools. These parts need to meet stringent quality standards, and Non-APC HMCs can provide the necessary precision and surface finishes, even if they are not as fast as APC-equipped machines. The manual load and unload process is manageable given the low production volumes in these settings.
Small-Batch Automotive Parts Manufacturing: For small-batch production of complex automotive parts, such as custom gears, engine components, or prototypes, Non-APC HMCs provide the precision needed without the cost associated with fully automated systems. These machines are suitable for shops that manufacture low quantities of automotive components or handle specialised orders where frequent setup changes are needed.
Heavy Equipment and Agriculture Parts Manufacturing: In heavy equipment or agricultural machinery manufacturing, Non-APC HMCs are used for producing parts like housings, frames, or brackets in small to medium production runs. These industries often demand precision in large, complex parts, and Non-APC HMCs can meet these requirements without the need for continuous high-volume output. The slower process is not a drawback in these applications where production speed is less critical than quality and accuracy.
Defence and Military Manufacturing (Low-Volume Precision Parts): Defence applications often involve producing complex, high-precision parts in low volumes. Non-APC HMCs are ideal for machining components like weapon parts, vehicle components, and aerospace defence parts where quality, not quantity, is paramount. The manual operation is more suited to the low-volume and highly specialised nature of defence manufacturing.

Bharat Fritz Werner Ltd. (BFW) is a pioneering name in machine tools, manufacturing solutions, and technological innovation.
Follow us on
PRODUCTS
RESOURCES
BFW UPDATES
Subscribe to get notified about latest events, new products, industry insights and other updates from BFW, directly to your inbox.

Trusted Global Manufacturing Technology Partner
Copyright 2026 © BFW, Designed & Developed by Appac Mediatech Pvt Ltd
Get Quote
Are you looking for a product or service offer? Let us know your requirements and we will get back to you soon.
We will get back to you soon
Download the brochure
Download our comprehensive product brochure and learn how our products should support your needs.



